Consumer’s Rights
Consumer Advocacy for Deathcare issues
- Funeral Consumers Alliance The national organization with which FCA of Idaho is affiliated.
- Idaho Attorney General’s Office Consumer Protection Unit
- Snake River Region Better Business Bureau
- Federal Trade Commission consumer information on funerals and related matters, including:
- Facts for Consumers, your rights when buying funeral goods & services
- The more detailed Funerals: a Consumers Guide
- The text and detailed Information about the Funeral Rule, regarding availability of General Price Lists (GPL), what has to be on the GPL, etc.
- Internment.net has information about cemeteries around the world. You can browse by Idaho county from this list of Idaho cemeteries.
- Ada County Indigent Services Cremation Assistance; application must be filed before the cremation or burial services take place.

Health Care and Hospice Issues

- The Idaho Attorney General publishes Consumer Manuals, including a Senior Citizens Manual that includes overview information about end of life health care planning.
- The Secretary of State’s website has information about, forms for, and access to the Health Care Directive Registry. The information includes answers to frequently asked questions about the Registry, Living Wills, and the Durable Power of Attorney for Health Care.
- As of July 1, 2007, the Physician Orders for Scope of Treatment (POST) form provides a standardized form for expressing your wishes in advance of needing medical treatment. As explained in the Patient FAQs, A POST form is appropriate in cases where a patient has an incurable or irreversible injury, disease, illness or condition, or where a patient is in a persistent vegetative state. A POST form is also appropriate if such conditions are anticipated. The state Health and Welfare Emergency Medical Services website has links to more information, including instructions and a sample form.
Body and other Donations
- Informed Consent: What You Should Know When Donating Your Body, from Gere Fulton and Lamar Hankins, co-chairs of the Legal Committee of the national Funeral Consumers Alliance.
- Organ and Body Donation – A Gift to Science; info from the national FCA
- Idaho State University’s Anatomical Donation program supports their mission of education in many health-related fields. More information from the ISU website, or (as of mid-2019)
Idaho State University
Anatomical Donation Program
Department of Biological Sciences
921 S. 8th Ave. Stop 8007
Pocatello, ID 83209-8007
For more information:
(208) 282-4150
Email: Jackie Coffin at coffjacq@isu.edu
- Pacemakers: Pace4Life or Project My Heart Your Heart
- Hearing aids and Eyeglasses: Idaho Lions Foundation
Idaho Law and Legislation
- The Idaho State Board of Morticians website includes information for filing a complaint, and links to licensure law and rules, meeting notices, agendas and minutes.
- The Idaho Legislature
- Idaho Statutes
- Idaho statutes, Title 54, Chapter 11, Morticians, Funeral Directors and Embalmers
- Idaho statute Title 39, Chapter 45: The Medical Consent and Natural Death Act
- Rules of the State Board of Morticians (PDF)
- Idaho Legal Aid Services is a nonprofit Idaho law firm with offices throughout the state, working to seek equal justice for the underprivileged and poor through legal representation, community outreach, and education.

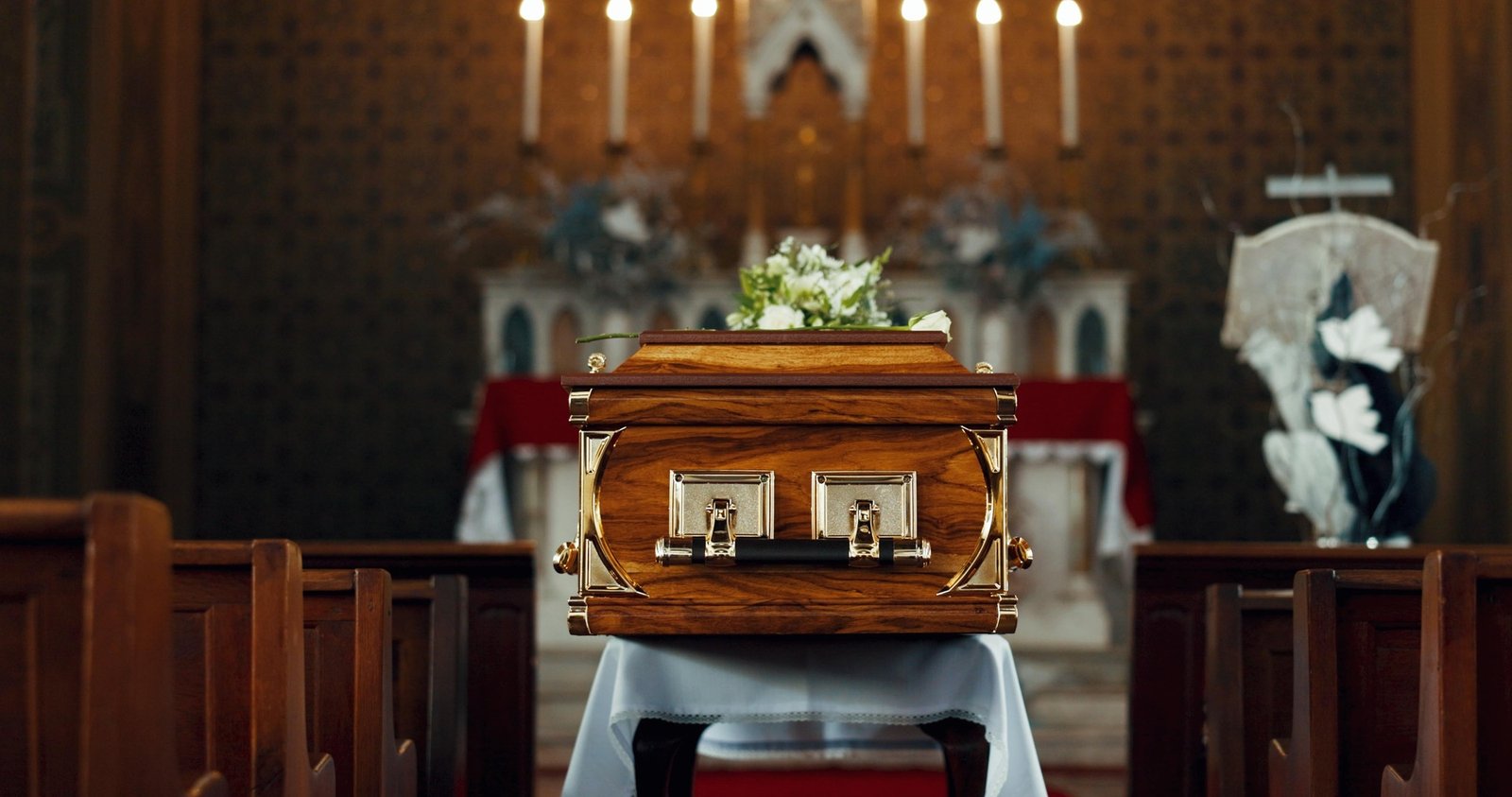
Funeral Arrangements
You may name an agent for body disposition if you want someone other than your next-of-kin to be in charge. A person may also establish preferences in a prepaid funeral plan.
It is legal for a family or designated agent to handle everything without a funeral director. To find a home funeral guide, check: http://homefuneraldirectory.com/
If you are working with a funeral home, prices must be given over the telephone. You must be given a General Price List (GPL) if you visit in person and before discussing any services
You must be given a Casket and Outer Burial Container Price List before selecting either.
The nonprofit consumer group in Boise does a price survey every year or two. www.fcai.fortboise.org
Do not sign any contract for more than you can afford to pay. If the deceased was indigent, there may be county funds but probably less than $1,000. There is no other organization that assists with costs.
Autopsy
- If the death was unexpected or the cause of death uncertain, the state will probably require an autopsy.
- If you have questions about the death, you may request and pay for a private autopsy
- A coroner or FBI agent in charge of investigation may, with a bit of debate, pay for the autopsy repairs when the autopsy is ordered by them and not by the family.
Organ, Body, and Tissue Donation
If death occurs in the hospital, you are likely to be asked about organ donation. Only about 1% of the deaths are eligible for major organ donation. The organ procurement organization (OPO) will pay for any extra body preparation needed if you plan a viewing. Decline any such charge you might find on the GPL.
After-death donation of eyes, skin, and bones may be considered. Ask the hospital social worker or the funeral director about this.
Whole body donation to a medical school is one way to cut costs although the family must pay for transportation to either med school in this state.
After study, the school will cremate the body and return the cremated remains to the family if requested. You should have back-up funeral plans if your body cannot be accepted for any reason.
There are also non-academic companies that accept whole bodies for research and education. Various body parts will likely be shipped around the country and possibly internationally. The state has no laws regulating these companies. Note that this is an entirely different category of body donation from the traditional cadaver donation to a medical school.
To find the nearest body donation option, the cost if any, and the reasons for body rejection check: www.finalrights.org
Embalming
A regulation, not a statute, requires embalming or refrigeration after 24 hours. This does not apply to home funeral families, only licensees.
Bodies transported by common carrier must be embalmed.
Many funeral homes have a policy that requires embalming for a public viewing. Embalming does not protect the public health. It merely delays decomposition.
Caskets and Vaults
- Neither are required by state law for burial. A rigid combustible container is required for cremation
- A casket will not prevent natural decomposition
- You may build your own or purchase from a casket retailer. Vault dealers rarely sell to the public
- The purpose of a vault is to keep the ground from caving in. It facilitates maintenance for the cemetery. It has no preservative qualities regardless of how much you spend.

Health Care and Hospice Issues

- Home burial is permissible in Idaho, but check local zoning laws first. A good practice is 150 feet from a water supply and 25 feet from a power line with two or three feet of earth on top. You should draw a map of the land showing where the family cemetery is and have it recorded with the deed.
- If you purchase a lot in a commercial, town, or religious cemetery, you will have the opening and closing costs in addition to the cost of the plot.
- Some cemeteries have restrictions on the kind of monuments permitted or plantings and adornment.
- A disinterment permit must be obtained from the state registrar. Disinterment must be under the supervision of a licensed funeral director.
Body and other Donations
- A coroner’s permit is required.
- A pacemaker must be removed
- Some crematories will let the family witness the cremation.
- One may authorize one’s own cremation in a preneed contract.
- The cremation process takes about two-and-ahalf hours for an average adult. The staff will remove any metal and pulverize the bone fragments to small particles, similar to white or gray coarse sand, about 5-10 pounds.
- Cremated remains may be kept at home, scattered on private land with the land-owner’s permission, interred in a cemetery or memorial garden, or placed in a mausoleum niche. If scattering on public land or water, don’t ask, don’t tell. Park service people are concerned that some may want to create a little shrine at the site and would prefer not to know your plans. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) says they must be scattered three miles out to sea. That’s because the federal agency has no jurisdiction over the first three miles; the bordering state does. Most states (except for California and South Dakota) have no restrictions on the disposition of cremated remains, and there are no “cremains police” even in those two states. Do as you wish.
- If flying with cremated remains, be sure they are in a non-metal container to pass through the scanner.
- Cremated remains may be sent only by U.S. Postal Service. Use certified mail. FedEx and UPS will not knowingly accept cremated remains.
Veterans and Their Dependants
- You will need a copy of the DD214 discharge papers for gaining benefits.
- There is a state-run veterans cemetery in Boise. Interment and marker are free of charge for the veteran, spouse, and certain dependants
- The U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) provides markers for veterans no matter where they are interred. Markers can be upright or flat, and they come in bronze, marble, and granite: (800) 697-6947.
- A free flag can be ordered through the U.S. Postal Service
- A comprehensive list of veterans benefits can be found here: www.funerals.org/faq/60-veteransfuneral-and-burial-benefits
Social Security Death Benefit
There is a $255 death benefit for a surviving spouse. There is no similar benefit when that spouse dies.
Dependent children are entitled to survivor benefits when a parent dies.

Prepaying for a Funeral
If the contract guarantees the price, the interest is supposed to cover funeral inflation. But many investments do not appreciate as fast as the prices climb. Some funeral homes will honor that guarantee regardless, and any substitutions should be of equal quality to that described in the contract.
Third-party items such as the crematory fee or obituary cannot be guaranteed.
If you move or cancel, you’re at risk of losing 15% and some of the interest.
Warehousing can avoid any trust requirements for cemetery merchandise, making a refund impossible
Setting aside assets for Medicaid eligibility is the one time it makes sense to prepay for a funeral. There is no limit to the amount in an irrevocable preneed trust. Be sure to ask if you will be getting an annual report of your prepaid funds and let those who will be handling your affairs know that you have prepaid and where.

Body and other Donations
- Valid complaints include dishonesty, misrepresentation, unprofessional conduct, negligence, breach of contract, violation of state or federal laws. For how to file a complaint, see www.funerals.org/your-legal-rights/complaint
- To file a complaint: www.ibol.idaho.gov Much of the information for this brochure was taken from
- Final Rights: Reclaiming the American Way of Death (Upper Access, 2011)
www.finalrights.org
Additional information may be found at www.funerals.org.
Prepaying for a Funeral
| Pros | Cons | |
|---|---|---|
| Pay on Death Savings Account or Bank CD |
|
|
| Qualified Funeral Trust |
|
|
| Master or Simple Trust |
|
|
| Funeral or Insurance |
|
|
